On this page
The Google Maps Distance Matrix API is a standard tool for calculating travel times and distances between multiple points. However, its complex pricing, usage limits, and closed data model often make it difficult to scale cost-effectively.
Geoapify provides a reliable and affordable alternative to Google Maps API Distance Matrix. Its Distance Matrix API supports:
- Multiple transport modes (drive, truck, walk, bike, transit)
- Large matrices with async processing
- Transparent pricing and predictable cost per request
Geoapify’s RESTful interface closely mirrors Google’s API, allowing for simple migration with minimal code changes. It’s fully compatible with JSON-based workflows and modern frameworks.
Powered by OpenStreetMap, GTFS, and other open datasets, Geoapify ensures global coverage, GDPR compliance, and no vendor lock-in.
What Is a Route Matrix (Distance Matrix) API
A Route Matrix API — also known as a Distance Matrix API — is a service that calculates travel times and distances between multiple origins and destinations. Instead of computing routes one by one, it processes all combinations in a single request, returning results in a matrix format.
Here’s an example of a 6×6 route matrix where origins and destinations are different named locations — for instance, distribution centers and delivery points in a city. Each cell contains both travel time (minutes) and distance (kilometers) estimated between the two points.
| From / To | Downtown | Airport | Shopping Mall | University | Industrial Park | Train Station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warehouse A | 12 min / 4.8 km | 25 min / 18.6 km | 10 min / 5.2 km | 17 min / 9.3 km | 8 min / 4.1 km | 14 min / 6.9 km |
| Warehouse B | 15 min / 6.5 km | 22 min / 17.2 km | 13 min / 7.4 km | 19 min / 10.5 km | 6 min / 3.2 km | 11 min / 5.8 km |
| Office HQ | 8 min / 3.5 km | 20 min / 16.0 km | 6 min / 2.8 km | 14 min / 8.0 km | 10 min / 5.1 km | 7 min / 3.9 km |
| Depot 1 | 18 min / 9.1 km | 27 min / 19.4 km | 12 min / 6.3 km | 9 min / 4.2 km | 5 min / 2.6 km | 13 min / 7.0 km |
| Depot 2 | 20 min / 10.2 km | 15 min / 12.3 km | 17 min / 9.7 km | 12 min / 6.5 km | 8 min / 4.0 km | 10 min / 5.2 km |
| Service Center | 10 min / 5.0 km | 23 min / 17.8 km | 9 min / 4.4 km | 15 min / 8.1 km | 7 min / 3.3 km | 0 min / 0 km |
This example illustrates how a Route Matrix API provides complete travel data between different origins (e.g., warehouses, depots) and destinations (e.g., commercial or public locations) in a single structured response. Such matrices are used in delivery optimization, logistics scheduling, and accessibility analysis, allowing systems to select the fastest or most efficient routes automatically.
Why Geoapify Is a Great Alternative to Google Maps API Distance Matrix
Before choosing a Distance Matrix API, it’s important to understand how much control you have over route calculations and how easily you can adapt them to your specific needs. The example below shows how a route matrix visualizes travel times and distances between multiple points — a common use case for logistics, accessibility analysis, and travel-time mapping.
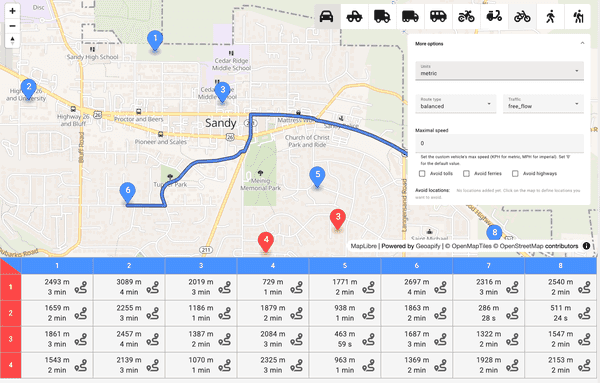
- Customizability
The Geoapify Route Matrix API is highly flexible and can be adjusted to fit almost any use case — from route optimization for delivery services to accessibility or travel-time analysis. You can easily define how routes are calculated, which roads to use or avoid, and how detailed the results should be.
| Parameter | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| mode | Selects the type of transport used for calculations. | drive, truck, bicycle, walk, transit |
| avoid | Lets you exclude specific road types or locations, such as tolls, highways, or custom areas. | avoid: [{"type": "tolls"}, {"type": "highways"}] |
| traffic | Adjusts travel times based on traffic conditions. | traffic: "approximated" |
| type | Defines route preference: shortest, fastest, or fewer turns. | type: "short" |
| max_speed | Sets the maximum allowed vehicle speed to reflect real driving or fleet limits. | max_speed: 80 |
| units | Specifies whether distances are shown in kilometers or miles. | units: "imperial" |
These options make the API easy to adapt to real-world scenarios. You can calculate routes that avoid tolls, simulate slower traffic conditions, or match local driving rules — all while maintaining consistent, accurate results based on OpenStreetMap and GTFS data.
- Affordable Pricing
Pricing is often the deciding factor when selecting a Distance Matrix API. Both Google and Geoapify offer scalable options, but their pricing models and matrix size limits differ significantly.
While Google Maps Distance Matrix API charges per element (each origin–destination pair), Geoapify uses a fairer calculation formula based on the number of origins and destinations:
cost = max(sources, targets) × min(sources, targets, 10)
This means that even for large matrices, the total number of billable elements — and therefore the cost — is usually much lower than with Google.
Here’s a comparison of the most affordable API plans:
| Plan | Free Tier | Mid Tier | Advanced Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Maps Distance Matrix API | 10,000 elements/month (≈333 per day) | 90,000 elements/month (≈3,000 per day) — $400/month | 300,000 elements — $1,250/month; 750,000 elements — $2,800/month |
| Geoapify Route Matrix API | 90,000 elements/month (≈3,000 per day) — Free | 300,000 elements — €49/month (API10 plan) | 750,000 elements — €89/month (API25 plan) |
Prices are approximate and based on public documentation as of 2025.
Official pricing pages: • Google Maps Platform pricing: https://mapsplatform.google.com/pricing/#pay-as-you-go • Geoapify pricing: https://www.geoapify.com/pricing/
Geoapify’s Free plan already includes up to 90,000 elements per month — nine times more than Google’s free quota — making it a practical choice for testing, small projects, or startups. Paid plans remain highly affordable, even for large-scale applications.
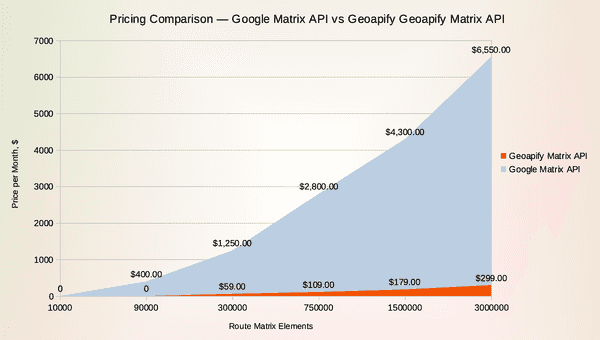
In addition, pricing transparency is built into Geoapify’s model: no hidden costs, no billing surprises, and predictable monthly usage.
- Matrix Size and Scalability
Matrix size limits directly affect both performance and cost. Google Maps Distance Matrix API supports up to 25 × 25 (625 elements) per request. Larger matrices must be split manually into multiple requests — which increases both complexity and billing, since Google charges per element (each origin × destination pair).
Geoapify supports larger matrices and a more cost-efficient calculation:
| Provider | Max Sync Matrix | Max Async Matrix | Cost Basis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Maps | 625 elements | Not available | Every origin × destination |
| Geoapify | 1,000 elements | Up to 3,000 elements | max(sources, targets) × min(sources, targets, 10) |
Because Geoapify uses the formula
cost = max(sources, targets) × min(sources, targets, 10)
it often reduces the number of billable elements — especially when calculating large matrices or when one side (origins or destinations) is smaller.
Even larger matrices can be combined easily using async processing, making Geoapify more suitable for delivery routing, location ranking, or accessibility calculations at scale — with predictable and lower costs.
- Variety of Related Products and API Solutions
A Distance Matrix API is often just one part of a complete location-based solution. Geoapify provides a broader ecosystem of APIs that work together using a unified data model, authentication, and routing logic — making it easier to build routing, accessibility, logistics, or analytical applications end-to-end.
| API | What It Does | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Route Optimization API | Builds and optimizes multi-stop routes | Fleet routing, courier scheduling, technician dispatch |
| Routing API | Generates navigable routes and turn-by-turn directions | Navigation, ETA calculation, mobile routing apps |
| Geocoding & Reverse Geocoding | Converts addresses ↔ coordinates | Address validation, customer location processing |
| Isoline API | Creates reachable areas based on travel time or distance | Service coverage, accessibility analysis, catchment studies |
| Static Maps API | Generates map images with routes, markers, or isolines | Reports, dashboards, PDFs, route previews |
Using these APIs together, you can:
- Calculate time and distance matrices
- Optimize delivery or service routes
- Build fleet management and routing dashboards
- Generate travel-time accessibility zones (Isoline API)
- Convert addresses and visualize results on static or interactive maps
This ecosystem makes Geoapify suitable for logistics, mobility, transportation planning, business location analysis, and digital mapping applications — without using multiple providers or complex integrations.
Geoapify vs Google Distance Matrix API — Feature Comparison
Both APIs serve the same core purpose — calculating travel time and distance between multiple origins and destinations — but they differ in flexibility, pricing model, matrix size, and traffic handling.
| Feature | Google Distance Matrix API | Geoapify Route Matrix API |
|---|---|---|
| Input structure | origins[] and destinations[] (placeId, address, or coordinates) | sources[] and targets[] (coordinates only — [lon, lat]) |
| Max matrix size (single request) | 625 elements (25×25) | 1,000 elements (sync), up to 3,000 elements (async) |
| Traffic support | Live and predictive traffic (TRAFFIC_AWARE_OPTIMAL) | Approximated traffic using speed reduction on busy roads |
| Transport modes | DRIVE, BICYCLE, WALK, TRANSIT, TWO_WHEELER | drive, truck, bicycle, walk, transit, and more |
| Route preferences | TRAFFIC_AWARE, FUEL_EFFICIENT, etc. | balanced, short, less_maneuvers |
| Road avoidance options | Not explicit, but can avoid highways/tolls via route parameters | Avoid highways, tolls, or custom locations (polygons or coordinates) |
| Cost calculation | Per element (origins × destinations) | max(sources, targets) × min(sources, targets, 10) (much lower) |
| Language / units | Supports languageCode, regionCode, units | Supports units, relies on language-neutral results |
| SDK support | Strong (JavaScript, Python, Node.js, Mobile) | REST API + SDK/CLI examples, works with any stack |
| Data foundation | Proprietary Google Maps data | OpenStreetMap, GTFS, elevation, open data |
Key Takeaways
- Google uses a strict element-based billing model, while Geoapify charges less by using a cost formula, significantly reducing cost for larger matrices.
- Geoapify supports larger matrices (up to 3,000 elements per request) and offers async processing, while Google requires splitting.
- Geoapify offers more control over routing behavior, including custom avoid areas, vehicle speed limits, and service zones.
- Google provides real-time traffic models, while Geoapify offers traffic approximation using road load estimation — suitable for planning and estimation.
- Google supports placeId and address input, Geoapify works directly with coordinates, making it lightweight for API and backend workflows.
How to Migrate from Google Maps Distance Matrix API to Geoapify
Migrating from Google Maps Distance Matrix API to Geoapify is straightforward because both APIs follow a REST-based structure and return JSON responses. In most cases, migration requires adjusting the endpoint, renaming parameters, and replacing place IDs or addresses with coordinates.
Step 1. Replace Endpoint URL
Google:
https://routes.googleapis.com/distanceMatrix/v2:computeRouteMatrixGeoapify:
https://api.geoapify.com/v1/routematrixStep 2. Replace Origins/Destinations with Sources/Targets
Google accepts origins and destinations as placeId, address, or coordinates.
Geoapify uses coordinates in sources and targets arrays, formatted as [lon, lat].
Google style:
"origins": [
{"address": "1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA"}
],
"destinations": [
{"address": "1 Market St, San Francisco, CA"}
]Geoapify style:
"sources": [
{ "location": [-122.084, 37.422] }
],
"targets": [
{ "location": [-122.394, 37.794] }
]If your application uses addresses or place IDs, simply geocode them using the Geoapify Geocoding API before making matrix requests.
Step 3. Replace Parameter Names
| Google Parameter | Geoapify Equivalent |
|---|---|
origins | sources |
destinations | targets |
travelMode | mode |
routingPreference | type |
trafficModel | traffic |
units | units |
departureTime | Not required (Geoapify uses approximated traffic) |
Step 4. Selecting Travel Mode
| Geoapify | |
|---|---|
DRIVE | drive |
TWO_WHEELER | scooter, motorcycle |
TRANSIT | transit |
WALK | walk |
BICYCLE | bicycle, road_bike, mountain_bike |
Step 5. Example Migration
Google Distance Matrix Request (simplified):
{
"origins": [{"latLng": {"latitude": 37.422, "longitude": -122.084}}],
"destinations": [{"latLng": {"latitude": 37.774, "longitude": -122.419}}],
"travelMode": "DRIVE",
"routingPreference": "TRAFFIC_AWARE_OPTIMAL"
}Geoapify Route Matrix Request:
{
"mode": "drive",
"traffic": "approximated",
"sources": [{ "location": [-122.084, 37.422] }],
"targets": [{ "location": [-122.419, 37.774] }],
"type": "balanced",
"units": "metric"
}6. Testing the Migration
You can test your requests using:
✔ Postman
✔ Browser (for simple GET requests)
✔ Command-line (curl)
✔ Geoapify API Playground (built-in in documentation)
Step 7. Adjust Matrix Size (Optional)
| API | Matrix Limit |
|---|---|
| 625 elements | |
| Geoapify | 1,000 sync / 3,000+ async |
If your matrices are larger, Geoapify allows async processing or even combining matrices without hitting cost spikes — thanks to the formula-based pricing.
Step 8. Keep Costs Low with Geoapify’s Billing Formula
Instead of charging per origin × destination pair like Google, Geoapify uses:
cost = max(sources, targets) × min(sources, targets, 10)
This means that even large matrices often cost less than expected, especially when one side (origins or destinations) is smaller.
✔ Migration Summary
| Migration Step | Effort |
|---|---|
| Change endpoint | Easy |
| Rename parameters | Easy |
| Switch addresses to coordinates | If needed (via Geocoding API) |
| Update transport modes | Mostly mapping values |
| Adjust pricing model | Automatic (more efficient) |
| Scale matrices | Easier with Geoapify |
Learn more
Looking to build routing, distance analysis, address validation, or interactive maps into your product? Geoapify provides developer-friendly APIs, SDKs, and ready-to-use components to help you launch faster.
You might also find these resources helpful:
Google Maps API alternative
Route Optimization Solutions

Logistics APIs | Delivery & Tracking Solutions
These articles will help you integrate routing, optimize logistics operations, create matrix-based travel-time calculations, or migrate away from Google Maps with minimal effort.
Conclusion
Google Maps Distance Matrix API is widely used, but its pricing model and matrix size limits make it challenging for scalable routing, logistics, and location-based applications. Geoapify offers a flexible and affordable alternative — with larger matrix sizes, full transport mode support, transparent pricing, and no vendor lock-in.
Explore Geoapify solutions:
Start for free and build location-aware applications with predictable costs and modern API tools.
FAQ
What is a Distance Matrix API and why would I need an alternative to Google Maps?
A Distance Matrix API calculates travel times and road distances between multiple origins and destinations in one request. The Google Maps Distance Matrix API is popular, but its pricing model and matrix size limits can become restrictive as your application scales. Geoapify’s Route Matrix API offers larger matrix sizes, transparent pricing, and more routing flexibility.
Is Geoapify Distance Matrix API free to use?
Yes. Geoapify offers up to 90,000 elements per month — around 3,000 elements per day — completely free. This makes it ideal for development, prototypes, academic projects, small business use, or testing before scaling. Details can be found on the pricing page.
How does Geoapify pricing compare to Google Maps Distance Matrix API?
Google charges per element (origin × destination), which becomes expensive for large matrices. Geoapify uses a simplified formula — max(sources, targets) × min(sources, targets, 10) — which often results in lower billable usage. This helps reduce cost, especially for routing, logistics, and location analytics applications. Compare plans on the Geoapify Pricing page.
How many origins and destinations can I calculate with Geoapify?
You can generate matrices up to 1,000 elements using synchronous API requests and up to 3,000+ elements with asynchronous processing. Larger matrices can be split and combined. Google Maps API is limited to 625 elements. More details on the Route Matrix API page.
Does Geoapify support traffic-based travel time calculations?
Geoapify provides an approximated traffic model that adjusts speeds on congested roads. While it does not offer live sensor-based traffic data like Google, it is suitable for route planning and estimation. You can enable it using traffic: "approximated" in the request.
Which transport modes are supported by Geoapify?
Geoapify supports driving, truck routing (light, medium, heavy, long), bicycle, road bike, mountain bike, walking, hiking, scooter, motorcycle, bus, transit, and approximated transit — and more. View full mode list in the Route Matrix API documentation.
Does Geoapify provide turn-by-turn directions or optimized routes?
Yes. Use the Route Planner API for multi-stop route optimization, and the Routing API for turn-by-turn navigation and instructions. These APIs work well alongside the Route Matrix API.
Can Geoapify fully replace Google Maps Distance Matrix API?
For most routing, analytics, delivery, mobility, and map-based use cases — yes. Geoapify offers a complete set of location APIs including matrix, routing, planning, geocoding, isolines, and static maps — using open data and transparent pricing. Learn more at Geoapify as a Google Maps API alternative.
How do I migrate from Google Maps Distance Matrix API to Geoapify?
Migration typically involves replacing the endpoint, adjusting parameters, and switching from place IDs/addresses to coordinates. Most integrations require minimal code changes. You can start by testing with Postman or the API Playground on the Route Matrix API page.