Extreme weather events are on the rise. According to the United Nations:
- Major floods have more than doubled
- Severe storms have risen 40 percent
- Droughts, wildfires, and heatwaves have all increased
We all need to be prepared for more extreme weather as wetter winters and drier summers become the norm. And that includes businesses.
Extreme weather events can have a huge impact on your business. From physical location damage to network outages, extreme weather can affect your ability to keep your business working as expected.
Being prepared is key to reducing risks and losses. Geospatial analytics, such as Geoapify, helps businesses with disaster management and planning.
What Is Geospatial Analytics?
Geospatial analytics is the analysis of geospatial data. Geospatial analysis is useful for disaster prevention.
What is geospatial data? Geospatial data is information about objects or events on or near the earth's surface. Geospatial data includes:
- Location information, for example the west coast of Scotland.
- Characteristics of the object or event, such as a rainstorm, flood, or wildfire.
- Time information such as when the event occurred and how long it lasted, such as a thunderstorm lasting 53 minutes.
Geospatial data can be about a fixed event like an earthquake, or an ongoing event like the spread of a disease.
Geospatial analytics means collecting all of that data, analyzing it, and visualizing it. Geospatial surveillance helps prepare for disasters and emergencies by putting the data into an accessible format. This is usually a graph, chart, or visualization.
Now it's easier to understand what the geospatial data means, and put it to practical use in disaster management and planning.
To explore the various types of geospatial data and their applications, check out our article on Different Geospatial Data Types.
How Does Geospatial Analytics Help Forecast Disasters?
Geospatial technology gives information about past and potential future weather events.
Geospatial surveillance can provide disaster and emergency preparedness data about:
- Climate
- Tides
- Wildfires
- Drought
- Vegetation
- Seismic activity
- Water levels
Geospatial analytics adds time and location information that makes geospatial data more effective for disaster management.
Maps, graphs and statistics show current activity and historical trends. You can see changes taking place over time in specific areas. Maybe one of your storefront locations is experiencing heavier rainfall year on year with more flood risk. Or perhaps one of your server farms is in a building that could be affected by wildfires.
Make use of past events and current trends
By combining current information with details about past events and trends, you can build up a fuller picture of the future. The more information you have, the faster and more accurate predictions you can make.
Environmental agencies are practiced at using geospatial techniques for disaster prevention. For example, an environmental agency might gather rainfall, water level, and climate data. Add in details about topography and ground conditions in a specific area, and they can create warnings about potential floods. They could even use past trends to predict floods that won't happen until a few days after rainfall stops.
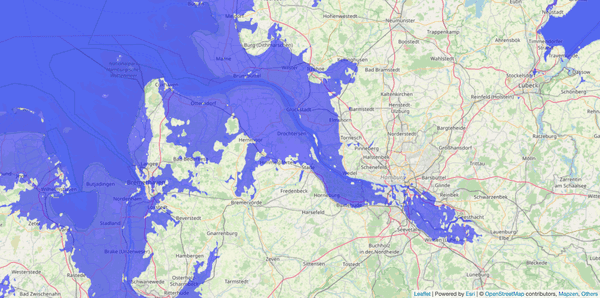
A flood map from floodmap.net. The image shows an area of Germany with different areas colored in green and purple
Businesses can also use geospatial data for better disaster management and preparation. You could use flood data to plan your flood response, and avoid shock if the flood comes after the initial rainfall.
What Difference Does Geospatial Analytics Make To Disaster Preparations?
Geospatial analytics gives you specific, easy to visualize, details. Armed with those details, your business can put contingency plans in place.
You can use geospatial data to track signs of impending disasters and emergencies by:
- Capturing early signs of storms or droughts.
- Gathering early warning pictures of landslides or sinkholes.
- Gathering data about vegetation state and density to highlight areas of deforestation. This can flag up where the conditions are ripe for wildfires or droughts.
Adding real-time data for more effective analysis
Historical data alone isn't as accurate as it used to be. Real world conditions are changing more rapidly than before. Adding real-time data makes for much more accurate analytics. Using both types of data, analysts can carry out predictive modeling.
Seeing what's coming helps businesses plan more effectively.
Geospatial techniques have already been shown to impact disaster recovery. When Hurricane Irma was heading to Florida, the city of Key West was prepared. Map-based data from previous storms helped them visualize the hurricane and put a solid storm preparation and damage control strategy in place.
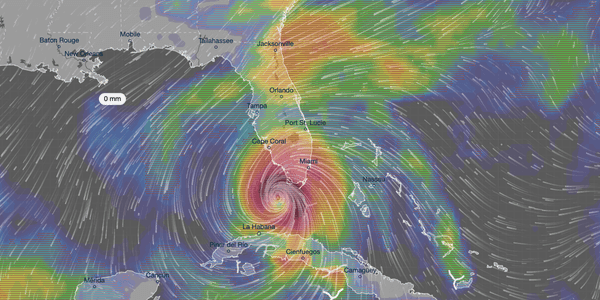
A visualization of Hurricane Irma on 10th September 2017 from ventusky.com. White lines show wind path and direction while colorization in red, orange, and green shows precipitation.
What Kind Of Businesses Can Use Geospatial Analytics In Disaster Preparedness?
According to the Carbon Disclosure Project, climate change risks will cost businesses up to US$120 billion in the next 5 years. So the more prepared you can be, the better.
Geospatial analytics has clear benefits for public health services, and environmental and disaster response agencies. But plenty of businesses can use geospatial data for disaster management.
- Utility companies can use geospatial surveillance to plan for potential outages due to extreme weather. They can schedule regular maintenance to avoid risky times, and schedule disaster-specific maintenance if needed.
- Government offices can predict and manage natural disasters in their local area. They can use data to alert businesses and tenants and give them time to prepare.
- Healthcare and maintenance businesses such as home care, home repairs, or IT maintenance, can plan schedules. They can decide when and where to send staff, avoid high risk times and areas, and help those in the path of disasters to prepare.
- Insurance firms can give more accurate quotes based on predictions and risk assessments.
- Travel and tourism companies can forewarn travelers and help them avoid at-risk areas and times.
- Transport firms can adjust routes or add diversions.
- Delivery companies can plan or change routes and schedules based on potential problems.
Business can't always prevent disasters, even with geospatial data. But they can plan better and reduce losses.
How Can Businesses Use Geospatial Analytics To Help With Disaster Preparation?
According to FEMA, 25% of businesses don't reopen after a disaster. Meanwhile, only 54% of businesses have a company wide disaster recovery plan in place. Better planning can help your businesses minimize losses, and survive a disaster. With geospatial analytics, you can track weather trends such as tornados or wildfires. You can look at the potential for flooding, droughts, or landslides. But what can you do with that information?
Build better disaster recovery plans
Armed with that information you can put together a disaster preparedness plan. Then if the worst happens, you're not scrambling to handle it. You can allocate resources before the disaster even occurs, reducing the shock of unexpected expenses.
And once the crisis has passed, you can analyze your disaster response plan and see where you need to make changes.
For example, if you're in an area with a wildfire risk, you can use geospatial analytics to see the predicted path of the fire. You can analyze which locations are at risk, how many sales you stand to lose, and how it will impact your supply chain. Now you can plan ahead to absorb those losses, change supply routes, or relocate staff.
Get all the info on new business locations
Before you open your business, or a new office or store location, check out the area. Use geospatial techniques to examine the potential for flooding, wildfires, and other disasters, before deciding whether to go there.
You can also examine existing locations and figure out if it would be safer and more cost effective in the long term to shift key centers to safer areas.

A map from arcgis.com that uses colored overlay to display geological suitability zones for urban planning, from the Cyprus Geological Survey Department. Numbers and shades of blue, green and bronze highlight areas of the map.
Shore up your existing assets
If you've got a store, warehouse, office or customer service center in an at-risk area, you can build resilience. Carry out risk assessments, and put together disaster plans. Look at whether you can install storm doors or shutters at your location, or assess if the building needs upgrades.
Keep staff and customers safe
Use geospatial techniques to optimize your supply and delivery routes. If you see potential floods or wildfires, you can assess whether it's safe to operate in that area, at that time.
For example, you can use isodistances and isochrones to calculate escape routes.
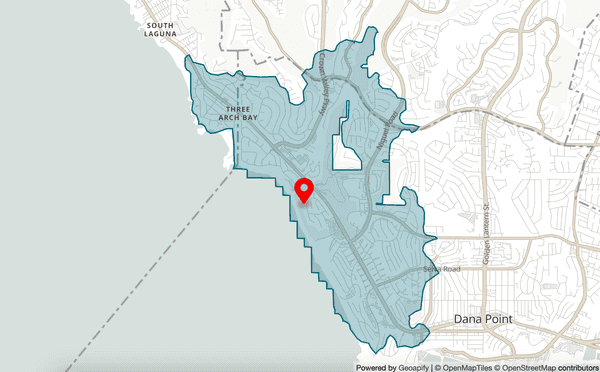
An image from Geoapify's Isolines Playground, showing isolines marked in dark teal around an area of Ritz Cove Drive, Dana Point, CA 92629, United States of America.
In the case of an event such as a tsunami, you can use isolines to show which escape routes are still possible based on the tsunami's progression. If it's still safe to proceed, you can build optimal delivery and supply routes to provide drivers with the safest way to their locations. If it's not safe, you can close locations to keep customers away, and let staff work from home.
Conclusion
The growing number of extreme weather events can feel alarming at times. But thoughtful application of geospatial techniques can help your business adapt, change and thrive in our changing world.
.jpg)